



Who Could be at Risk for Preeclampsia?
Preeclampsia is a serious condition that affects approximately 5-8% of pregnant women, usually after the 20th week of pregnancy. This condition causes high blood pressure along with signs of damage to another organ system, most commonly the kidneys.
What is Preeclampsia?
Preeclampsia occurs when the placenta does not receive enough blood flow, leading to problems with the mother’s blood vessels. This can result in elevated blood pressure and the presence of protein in the urine. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications, including eclampsia, which involves seizures and can be life-threatening.
Causes and Risk Factors of Preeclampsia
● First-time pregnancy: Women who are pregnant for the first time are at a higher risk.
● Obesity: Excess weight before pregnancy can increase the likelihood of developing preeclampsia.
● Age: Women over the age of 35 are more susceptible.
● Family History: A family history of preeclampsia can elevate risk levels.
● Multiple pregnancies: Carrying twins or more increases the risk.
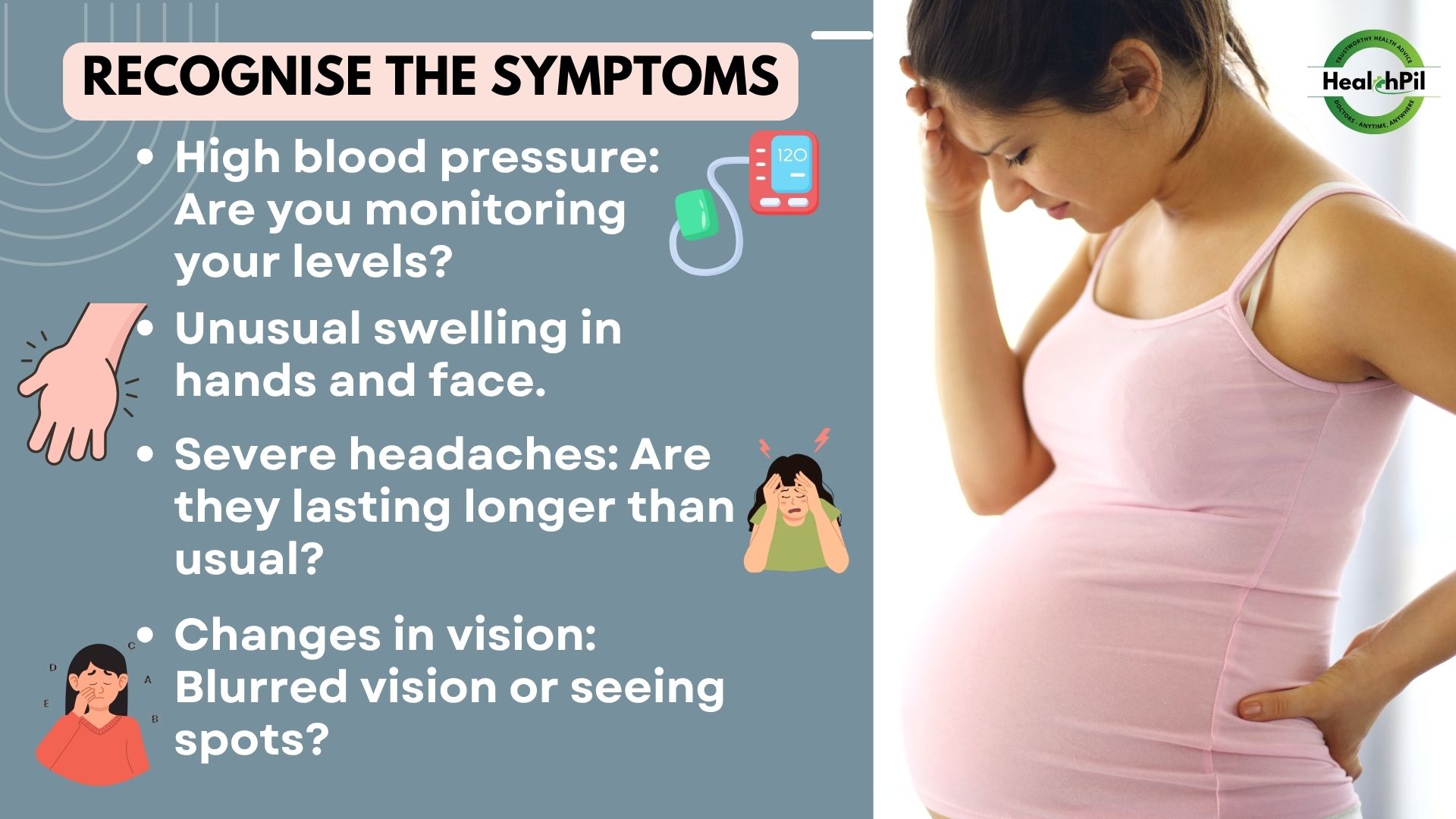
Recognizing Symptoms
● High blood pressure (140/90 mmHg or higher)
● Swelling in the hands and face
● Sudden weight gain
● Severe headaches
● Changes in vision, such as blurred vision or seeing spots
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s critical to seek medical attention immediately.
Diagnosis of Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is diagnosed through routine prenatal visits, during which healthcare providers monitor blood pressure and test urine for protein. If preeclampsia is suspected, additional tests may be performed to assess liver and kidney function and to check for signs of blood clotting disorders.
Potential Risks and Complications
If left untreated, preeclampsia can lead to serious complications for both the mother and baby, including:
● Eclampsia: A serious condition that can cause seizures and may be life-threatening.
● Organ Damage: The liver, kidneys, or other organs can be affected, sometimes leading to organ failure.
● Placental Abruption: The placenta may detach from the uterus, causing heavy bleeding and posing serious risks for both mother and baby.
● Low Birth Weight: Babies may be born underweight due to reduced blood flow during pregnancy.
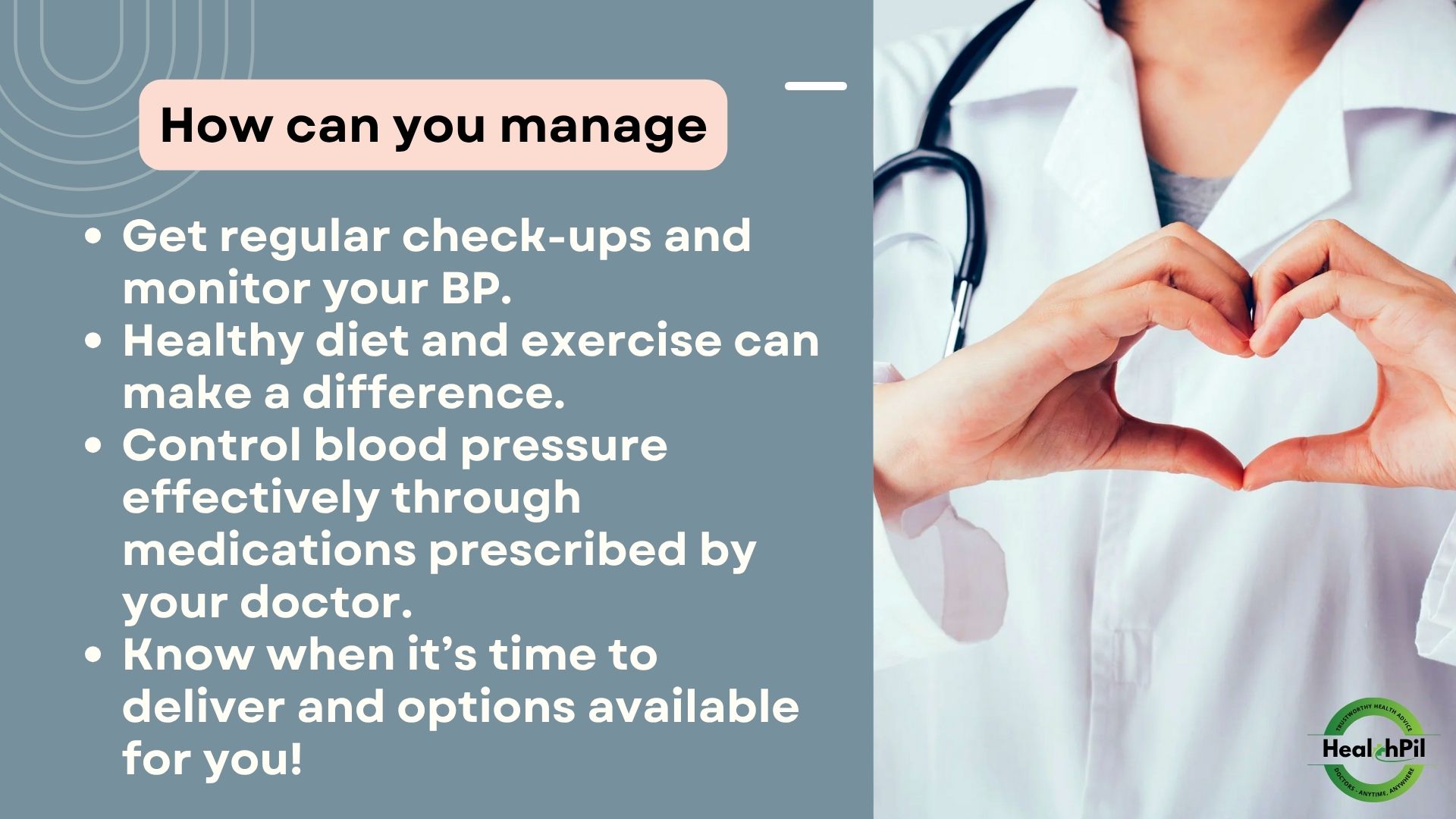
Management and Treatment of Pre eclampsia
1. Regular Check-ups:
Frequent prenatal visits to monitor blood pressure and urine protein levels are essential.
2. Lifestyle Modifications:
Maintaining a healthy diet, staying active, and managing stress can help mitigate risks.
3. Medications:
Antihypertensive medications may be prescribed to lower blood pressure, and magnesium sulfate may be used to prevent seizures in severe cases.
4. Delivery:
In some cases, the best way to treat preeclampsia is to deliver the baby. The timing will depend on the severity of the condition and gestational age.
Frequently Asked Questions
What increases the risk of developing preeclampsia?
Factors include being a first-time mother, obesity, age over 35, family history, and multiple pregnancies.
How is preeclampsia treated?
Treatment may involve lifestyle changes, monitoring, and medications. In severe cases, delivery may be necessary.
Can preeclampsia occur after childbirth?
Yes, women can develop postpartum preeclampsia within 48 hours of delivery.
What should I do if I suspect I have preeclampsia?
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience symptoms.
Conclusion
Preeclampsia is a serious condition that requires careful monitoring and management. By understanding the risks and symptoms, expectant mothers can take proactive steps to ensure a healthier pregnancy. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers are vital in navigating this journey.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for awareness purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized medical guidance.
How HealthPil can help?
HealthPil Is Always Here for YOU!
● Need Guidance? Connect with healthcare experts ready to help you navigate gestational diabetes.
● Join Our Community: Gain access to tips, resources, and support from mothers just like you!
● Don’t Delay—Take Action! Your health and your baby’s future are too important to wait!
Contact HealthPil today and empower your pregnancy journey!
