





What is Preterm Labor?
Preterm labor is the onset of contractions and cervical changes before 37 weeks of gestation. If not managed properly, preterm labor can lead to premature birth, which may pose risks for the baby, including developmental delays and other health issues.
Preterm labor is a significant concern that occurs when uterine contractions begin before 37 weeks of pregnancy. It affects about 1 in 10 births and understanding the signs and risk factors is crucial to ensuring a healthy outcome for your baby.
Causes and Risk Factors of Pre-term labor:
● Infections: Urinary tract infections or other infections can trigger contractions.
● Chronic Conditions: Health issues like diabetes or high blood pressure can elevate risk.
● Multiple Pregnancies: Carrying twins or more increases the chances of preterm labor.
● Previous Preterm Births: A history of preterm labor increases the likelihood of recurrence.
● Stress: High levels of physical or emotional stress can lead to early contractions.
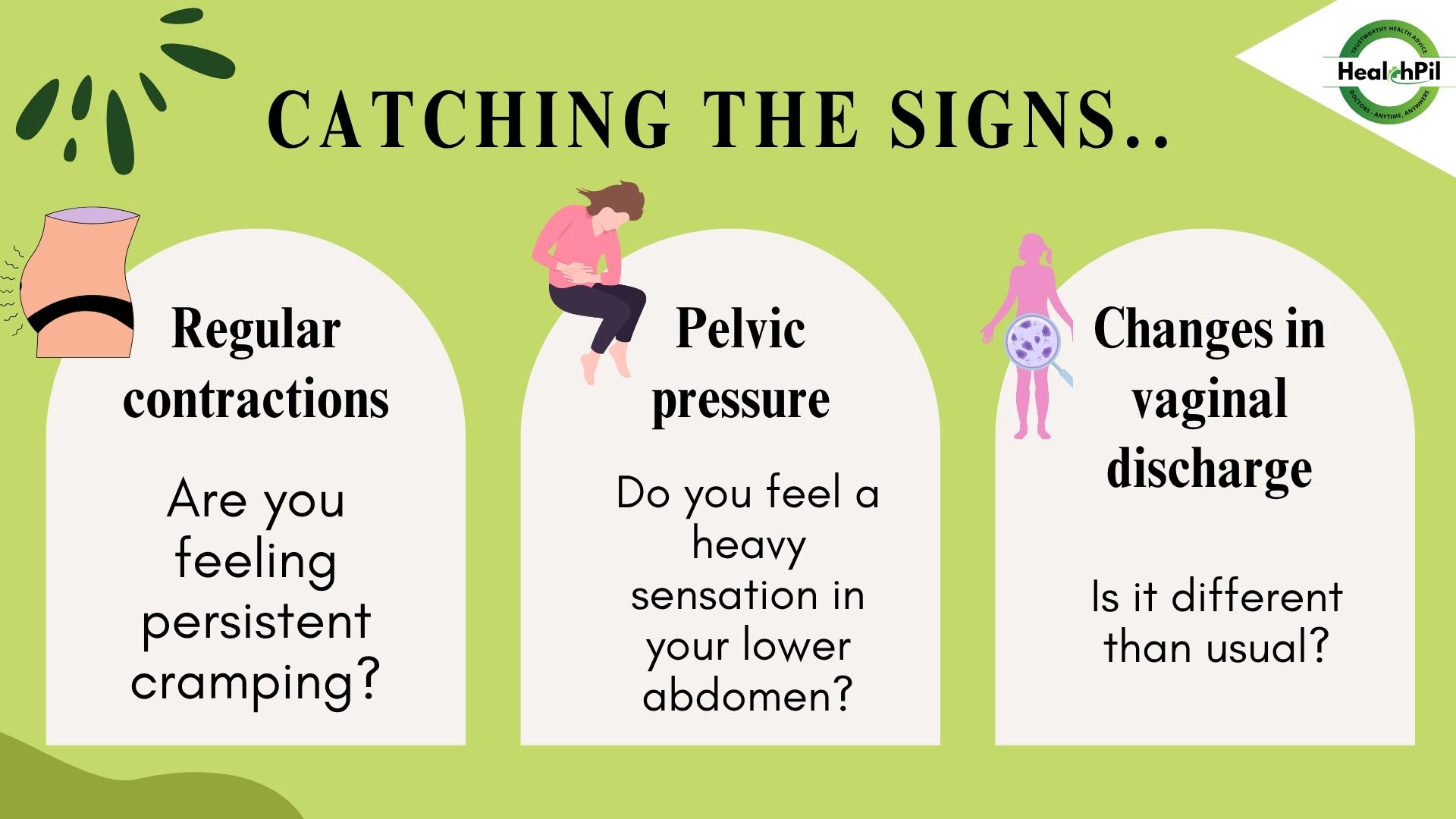
Recognizing Symptoms
Awareness of the symptoms is vital. Key signs of preterm labor include:
● Regular contractions or cramping
● Lower back pain that doesn’t go away
● Pelvic pressure or fullness
● Changes in vaginal discharge (increased or unusual)
● Abdominal cramps with or without diarrhea
If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Diagnosis of Preterm Labor
To diagnose preterm labor, your doctor will likely do a physical exam, monitor your contractions, and may use an ultrasound to check the length of your cervix. They might also perform a fetal fibronectin test to help gauge the chances of an early birth.
Potential Risks and Complications
Preterm labor can lead to several complications for both mother and baby, including:
● Premature Birth: Babies born before 37 weeks may face various health challenges.
● Low Birth Weight: Preterm babies are often smaller and may require special care.
● Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Preterm infants may have difficulty breathing due to underdeveloped lungs.
● Long-term Health Issues: Some preterm infants may experience developmental delays and learning difficulties.
Management and Treatment of Pre-term labor
Medical Intervention:
● Medications: Tocolytics may be given to help stop contractions.
● Corticosteroids: These can speed up the baby’s lung development if early delivery seems likely.
Lifestyle Modifications:
● Bed Rest: Your doctor might suggest limiting physical activity.
● Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough fluids can help prevent dehydration, which might trigger contractions.
Regular Monitoring:
● Frequent check-ups are important to keep an eye on both the baby’s growth and the mother’s health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of preterm labor?
Infections, chronic conditions, and multiple pregnancies are common triggers.
How can I prevent preterm labor?
Regular prenatal care, managing chronic conditions, and reducing stress can help minimize risks.
What should I do if I experience symptoms?
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you notice signs of preterm labor.
Can preterm labor affect my baby’s health?
Yes, premature birth can lead to several health complications, including developmental delays.
Is it possible to carry the baby to term after experiencing preterm labor?
In some cases, yes. Timely medical intervention can help manage the situation.
Conclusion
Preterm labor is a serious condition that requires immediate attention. By understanding the risks and recognizing the symptoms, expectant mothers can take proactive steps to protect their health and their baby’s well-being. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers are essential in navigating this journey.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for awareness purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized medical guidance.
