Have you been feeling unusually tired, gaining weight, or experiencing mood swings? Even though the thyroid is tiny, it has an important effect on energy levels, metabolism, and even mental health. Thyroid disorders, including hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), affect millions of people across the world and often go undiagnosed.
What is the Thyroid Gland?
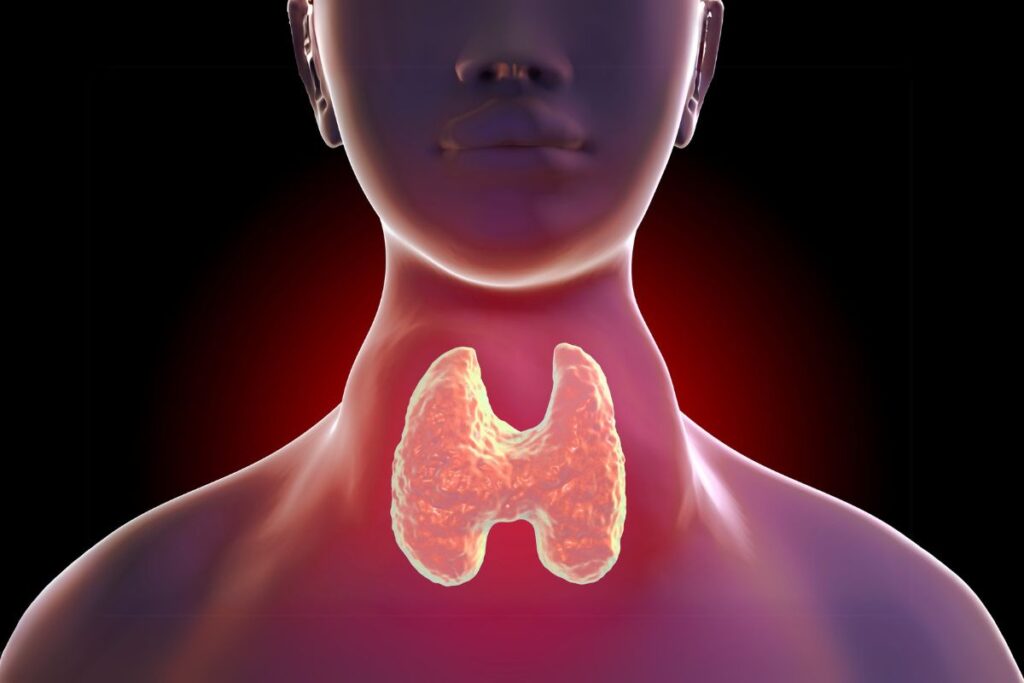
Located right below your Adam’s apple at the base of your neck, the thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland. Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), the thyroid hormones it produces, control many important body processes, such as:
● Metabolism: Your body’s process of converting food into energy.
● Body temperature: How your body maintains a stable temperature.
● Heart rate: How fast or slow your heart beats.
● Mood and cognitive function: affecting mental clarity, mood stability, and emotional well-being.
A number of symptoms that affect your general health and quality of life could result from the thyroid producing either too much or too little of these hormones.
Hypothyroidism: An Underactive Thyroid
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid doesn’t produce too many thyroid hormones, leading to a slowing down of various bodily functions. This condition is more common in women, particularly those over the age of 60.
Causes of Hypothyroidism:
1. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis:
The most common cause of hypothyroidism is an autoimmune disorder called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys thyroid tissue.
2. Iodine Deficiency:
In some parts of the world, a diet low in iodine can lead to an underactive thyroid.
3. Thyroid Surgery:
Removing all or part of the thyroid due to cancer or other thyroid diseases can lead to hypothyroidism.
4. Radiation Treatment:
Hypothyroidism can result from radiation therapy used to treat head or neck tumours because it damages the thyroid gland.
5. Medications:
Some medications, particularly those used to treat hyperthyroidism, can lead to hypothyroidism as a side effect.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism:
● Fatigue: One of the most common symptoms is feeling tired or exhausted.
● Weight Gain: Despite no change in diet, unexplained weight gain can occur due to a slowed metabolism.
● Cold Sensitivity: feeling cold all the time is a hallmark of hypothyroidism.
● Dry Skin and Hair: Your skin may become dry, and your hair may become brittle and fall out.
● Depression and Memory Problems: Hypothyroidism can affect your mental clarity, mood, and concentration.
● Constipation: Digestive problems like constipation might result from a slower metabolism.
Hyperthyroidism: An Overactive Thyroid
When the thyroid overproduces thyroid hormone, it causes hyperthyroidism, which speeds up a number of body processes. Even though it is less common than hypothyroidism, if treatment is not received, it can cause serious health problems.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism:
1. Graves’ Disease:
This autoimmune disease, in which the thyroid is stimulated to create an excess of hormones by the immune system, is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism.
2. Thyroid Nodules:
Benign nodules in the thyroid gland can sometimes produce excess hormones, leading to hyperthyroidism.
3. Thyroiditis:
Excess thyroid hormones may be released due to thyroid gland inflammation, which is sometimes caused by viral infections.
4. Excess Iodine:
Taking excessive iodine or certain medications can also trigger hyperthyroidism.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism:
● Weight Loss: unexplained weight loss despite increased hunger.
● Rapid Heart Rate: A fast or irregular heartbeat (tachycardia).
● Nervousness and Anxiety: Excess thyroid hormones can cause heightened anxiety, irritability, and mood swings.
● Increased Sweating: Feeling hot and sweating excessively.
● Tremors: Fine hand tremors are common in those with hyperthyroidism.
● Sleep Disturbances: Difficulty sleeping due to high metabolism and anxiety.
Diagnosing Thyroid Disorders:
A variety of imaging scans, blood tests, and physical examinations are used to diagnose thyroid problems. Thyroid diseases are diagnosed as follows:
1. Blood Tests:
● TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) Test: The primary blood test for diagnosing thyroid disorders. A high TSH level typically indicates hypothyroidism, while a low TSH level suggests hyperthyroidism.
● T4 and T3 Levels: Actual blood levels of thyroid hormones are found by the T4 and T3 tests. T4 and T3 levels that are low indicate hypothyroidism, whereas those that are high indicate hyperthyroidism.
● Antibody Tests: In cases of autoimmune thyroid disorders like Hashimoto’s disease or Graves’ disease, antibody tests can help confirm the diagnosis.
2. Imaging Studies:
● Ultrasound: An ultrasound can detect thyroid nodules or inflammation.
● Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test: This test helps to determine the cause of hyperthyroidism by measuring how much iodine the thyroid absorbs.
Treatment of Thyroid Disorders
Treatment for thyroid disorders depends on whether the thyroid is underactive or overactive.
Treating Hypothyroidism:
1. Thyroid hormone replacement:
Thyroid hormone replacement is the most popular treatment for hypothyroidism. Synthroid, a synthetic form of levothyroxine, is generally used to replace the affected thyroid hormone.
2. Dietary Adjustments:
For those with iodine deficiency, increasing iodine intake through diet (e.g., seafood, dairy, and iodised salt) can help.
3. Monitoring:
Regular blood tests are necessary to adjust medication dosages to keep TSH levels within the normal range.
Treating Hyperthyroidism:
1. Antithyroid Medications:
Medications such as methimazole (Tapazole) can prevent the production of thyroid hormones and reduce symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
2. Radioactive Iodine Therapy:
This treatment involves taking radioactive iodine, which is absorbed by the thyroid and destroys overactive thyroid tissue.
3. Surgery:
In severe cases, surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland may be necessary.
4. Beta-Blockers:
Medicines such as propranolol can help manage hyperthyroidism symptoms like tremors and an accelerated heartbeat.
FAQ Section:
Can thyroid disorders cause weight gain or loss?
Yes! Hypothyroidism can cause unexplained weight gain due to a slow metabolism, while hyperthyroidism can lead to weight loss despite an increased appetite.
Can thyroid disorders affect fertility?
Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can impact fertility. Hypothyroidism can cause irregular periods and difficulty conceiving, while hyperthyroidism can lead to ovulation problems.
Can thyroid problems cause hair loss?
Yes. Hypothyroidism often causes dry, brittle hair and hair loss, while hyperthyroidism can cause thinning hair.
How is thyroid disease treated?
Thyroid hormone replacement therapy is usually used to treat hypothyroidism, whereas medicines, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery can be used to treat hyperthyroidism.
Are thyroid disorders preventable?
While some thyroid disorders are genetic, many can be managed through early detection, regular checkups, and lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine.
Conclusion:
Thyroid problems are common, but they are so ignored that they can have a harmful effect on your health. Early diagnosis and treatment can help you take control over your health, regardless of whether you have an overactive or underactive thyroid. If you suspect you have a thyroid disorder, speak to your healthcare provider for an evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
For expert consultations and personalized care, visit HealthPil to connect with specialists who can help you manage thyroid disorders effectively.