




How ignoring headache caused seizure and diagnosis of a brain tumor
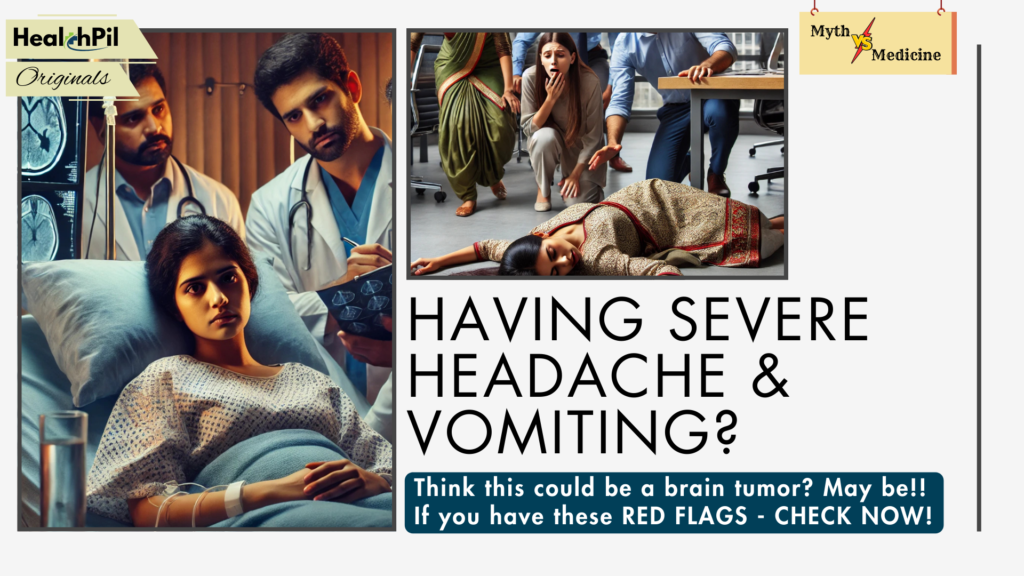
Neha, a 34-year-old woman, had been suffering from on-and-off headaches for several months. She also occasionally felt dizzy and experienced blurry vision but ignored it. Because the symptoms were irregular, she didn’t think it was serious enough to consult a doctor.
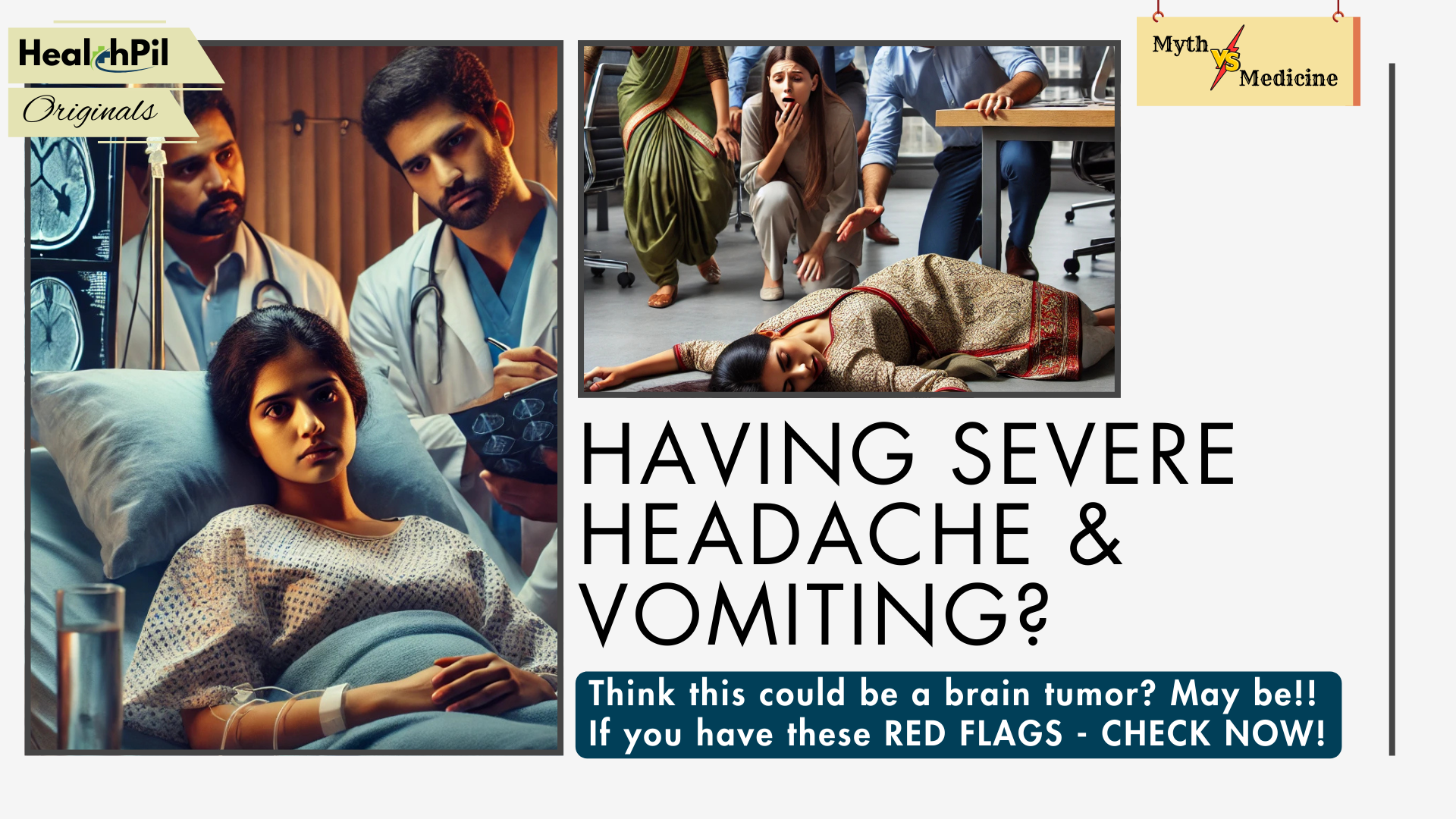
One day at work she fell down and threw a seizure. She was immediately rushed to a hospital; an MRI scan was done which revealed a brain tumor that had been silently growing for months. The tumor had pressed on important parts of her brain, requiring emergency surgery. Neha later learned that if she had addressed the headaches earlier, her tumor might have been found before the seizure happened, and the treatment may not have been so urgent.
What is a Brain Tumor?
A brain tumor forms when abnormal cells grow in or around the brain. These tumors can be either non-cancerous or malignant (cancerous). The symptoms they exhibit depend on the its size, shape, type and location in the brain.
Common Signs of Brain Tumors (Red Flags):
● Frequent or recurring headaches (new onset) or change in the character of headache
● Seizures happening repeatedly
● Blurred or double vision
● Persistent nausea or vomiting
● Difficulty with balance or coordination
● Noticeable personality changes or memory issues
The Risks of Ignoring Headaches and Seizures
In Neha’s case, her headaches were an early warning that something was wrong. The seizure happened because the tumor was putting pressure on her brain. Had she seen a doctor when the headaches began, the tumor might have been found and treated before it grew larger and triggered the seizure.
Treatment for Brain Tumors
- Surgery: For most brain tumors, surgery is the first step. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible without damaging vital brain tissue.
- Radiation and Chemotherapy: If a tumor is cancerous or not completely removable, radiation and chemotherapy may be necessary to target any remaining cells.
- Medication for Seizures: Patients like Neha, who develop seizures due to the tumor, may need medication to prevent future seizures.
- Regular Monitoring: Follow-up MRIs are needed after treatment to make sure the tumor doesn’t return or grow.
What Happens if a Brain Tumor Goes Untreated?
● Seizures and Brain Damage: Tumors can cause seizures, which may lead to long-term brain damage, affecting speech, movement, or memory.
● Increased Pressure in the Skull: Tumors can cause pressure to build up inside the skull, leading to serious problems like vomiting, severe headaches, and vision loss.
● Life-Threatening Complications: Without treatment, brain tumors can grow large enough to impact areas of the brain responsible for vital functions like breathing or heart rate, which can be fatal.
How HealthPil Can Help
If you or any of your loved ones has been experiencing frequent headaches, seizures, or other neurological symptoms, don’t wait to seek help. HealthPil provides access to expert neurologists who can offer guidance, diagnose the issue, and help you choose the right treatment plan.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are symptoms of a brain tumor?
Ongoing headaches, seizures, vision problems, and personality changes are some of the typical signs.
Can brain tumors be cured?
Benign tumors can often be removed with surgery, while cancerous tumors may require additional treatments like radiation and chemotherapy.
What happens if I ignore chronic headaches?
Ignoring persistent headaches could delay the diagnosis of a brain tumor, increasing the risk of seizures and other severe complications.
Can seizures indicate a brain tumor?
Yes, seizures can be one of the first signs of a brain tumor, especially in individuals without a prior history of epilepsy.
Disclaimer:
This article is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended to substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a doctor if you are experiencing persistent symptoms like headaches or seizures.